FAQ
PBCS is Oracle’s Planning & Budgeting Cloud Service.
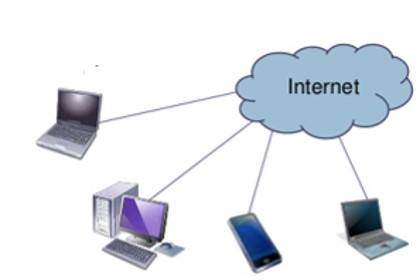
- A basic definition of cloud computing is the use of the Internet for the tasks you perform on your computer. The “cloud” represents the Internet.
- The physical infrastructure, or servers, of the Cloud (aka “the Internet”) are located in data centers around the U.S.
- Regular patches and upgrades now happen automatically, on a schedule.
- No longer necessary to buy or maintain on-site servers.
- Users and work groups can access all of their information anytime, from anywhere in the world.
- A database in the Cloud with a web address. All interaction with the Pod will be through a Browser.
- Ex: The internet location www.facebook.com is an application/database that exists in the Cloud.
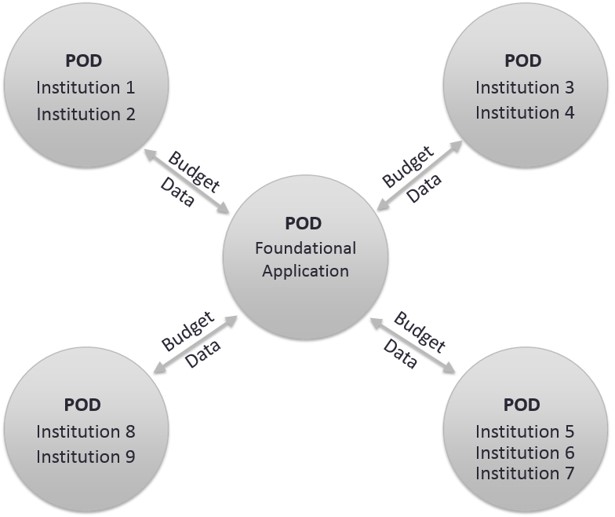
- Institution Pods will be built with the same architecture as the Foundational Pod, but the contents of the Pod can be configured to the preferences of the institutions included each Pod.
- The Foundational Pod receives and consolidates Budget data from all the Institution Pods.
Purpose:
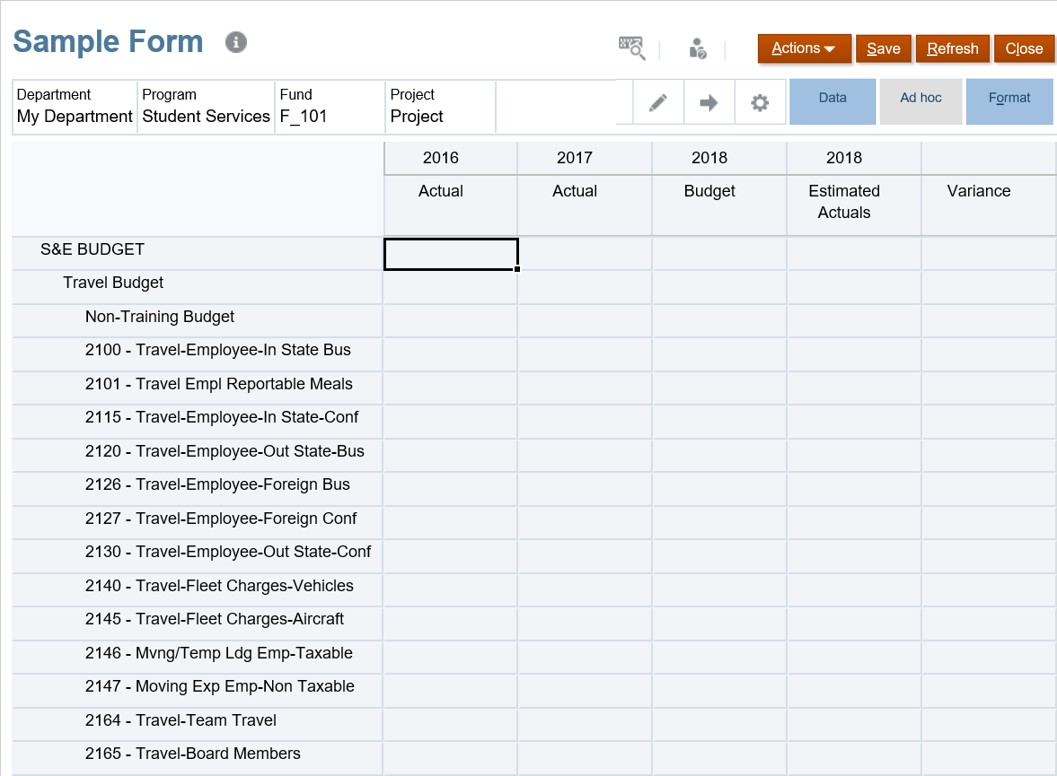
- A formatted, purpose built database ‘view’ for inputting or reviewing data.
- Structured similar to an Excel ‘grid’ view (rows, columns, page drop-down menus).
- Represents the main way in which users work with the tool
Scope of Use:
Can (and should) be used for a wide variety of purposes:
- Data input (lots of features)
- Data analysis (even more features, can be used as mock reporting)
- Workspace dashboards (combined input with immediate analysis)
- Execute Calculations
Dimension:
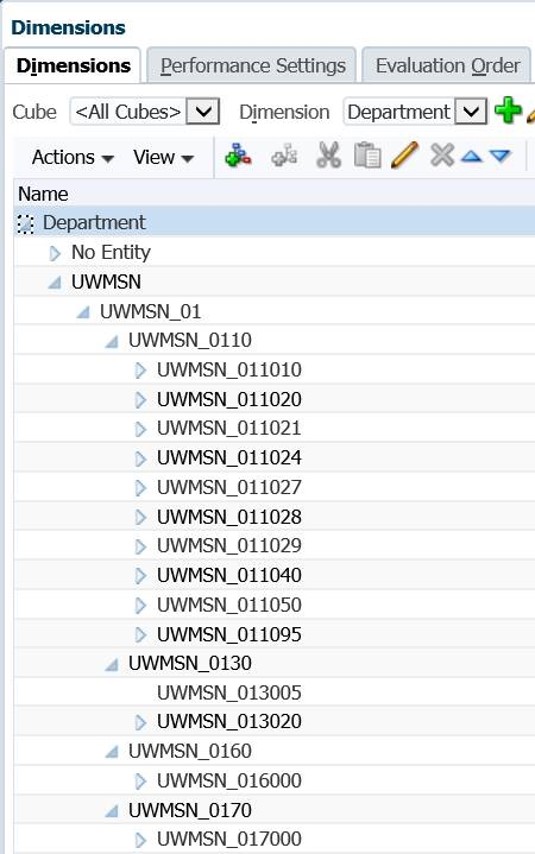
A Dimension is the hierarchical organization of a segment(s) of your GL Chart string. Similar to your CoA trees within SFS or WISER.
Example: Units, Divisions, Departments and Sub-Departments roll up to create the Department dimension.
Member:
Dimension Members are used to identify a data item’s position and description within a dimension, and they in turn make up a Dimension
Example: Sub-Department UWMSN_011010 is a member within the Department Dimension.
Purpose:
- Used to execute purpose built calculations and processes via commands.
- Can be extremely specific or have a broader purpose
Scope of Use:
Can (and should) be used for a wide variety of purposes:
- Data input validation (prevent human errors)
- Calculation of output (inputs drive outputs)
- Administrative tasks
- Data auditing
- Data management (maintaining data sets, scenarios/versions)